Llama 4 AI models, a new family of open-source models from Meta, are designed for both text and image processing, featuring a “mixture of experts” architecture for efficient processing and a large context window, enabling tasks like advanced image understanding, creative text generation, and general-purpose AI assistance.
Meta* has released a fresh generation of open Llama models. They stand out with a huge context of up to 10 million tokens, are optimized for coding, multilingual tasks, and the creation of autonomous systems (agents). In practice, however, the novelties turned out to be not as good as on paper. Let’s summarize the experts’ data.
Key Improvements and Features
All iterations of Llama 4 are built on the Moe (Mixture of Experts) principle. It is already used by many competitors, including DeepSeek V3 and Grok. This approach effectively uses the resources of the neural network, dividing it into several expert submodels. For each request, only a fraction of the total number of task-specific settings are activated. This improves the quality of answers while saving computing power. The three versions of the Llama 4 (small, medium and large) offer the following features:
- Llama 4 AI models Scout: 109B general parameters, 17B active, 16 experts. The context is 10 million tokens, which is 80 times more than Llama 3. Leadership in their class is declared in terms of reasoning, working with pictures (accepted up to five at a time), code and long context. In benchmarks, it is ahead of Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite, Mistral 3.1 and Gemma 3.
- Llama 4 AI models Maverick: 400B total, 17B active, 128 experts. The context is 1 million tokens. In terms of numbers, GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash are better, comparable to DeepSeek v3.1 in a smaller size. It reached the top of the LMArena ELO rating with a score of 1417.
- Llama 4 AI models Behemoth: 2 trillion common parameters, 288B active, 16 experts. It is in development and is not yet available to the public. With its help, two small versions were taught. In STEM benchmarks, it outperforms GPT-4.5, Claude Sonnet 3.7 and Gemini 2.0 Pro.
The systems are multimodal, that is, they are able to perceive text, images and video. 12 languages are supported, although Russian is not among them. In the line, alas, there is no folk modification of the model that could be launched on consumer hardware. Even the younger Scout requires at least 80 GB of video memory, which allows it to function only on a single H100 GPU with 4-bit quantization. The release is now limited to instant Instruct output, but later the developer will introduce Llama 4 with the Reasoning feature.
Nuances in independent tests
As it turned out, Maverick’s achievements on the LMArena portal may not be entirely objective, since the behavior of the model on the site is very different from the public version on Hugging Face. This means that the testers were provided with a different version of the neural network tailored to communication. Programming benchmarks also show contradictory results: even the compact Qwen2.5-coder 32B beats Llama 4, not to mention DeepSeek V3. In some cases, the predecessor Llama 3.3 70B was ahead.
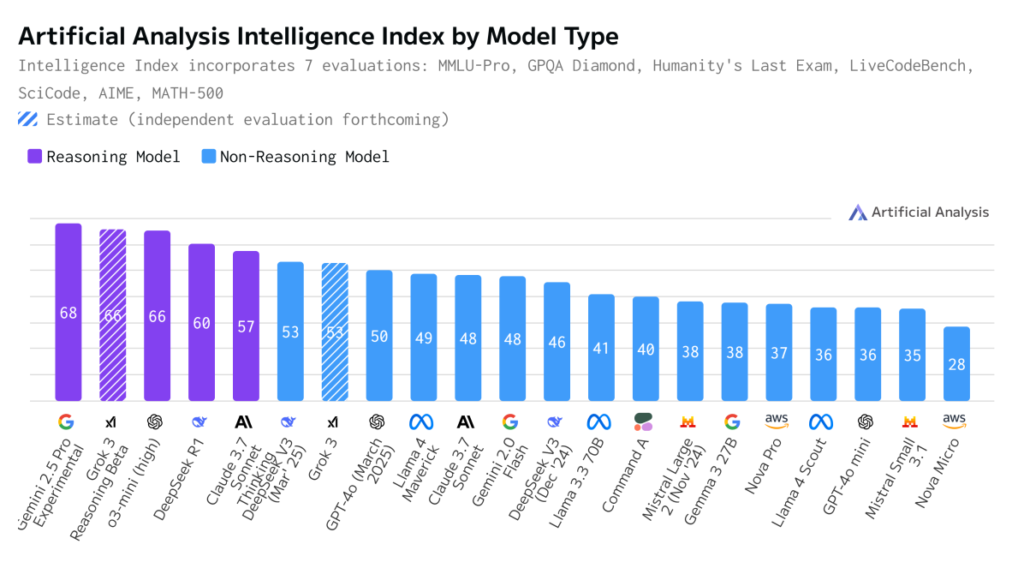
With regard to the long context, not everything is smooth either. The company admitted that directly during the training, the context provided did not exceed 256 thousand tokens. And it was expanded to 10 million after the fact. As a result, there are problems in the scenarios that assess the emotional intelligence of the LLM and the ability to process large texts. An even more visual representation of the quality of Llama 4 is provided by the complex metric Artificial Analysis Index. In it, the novelty is inferior to almost all current competitors, occupying ninth place.
Probably, further optimization of the service will help improve the situation. The creators explained that the temporary difficulties are caused not by the limitations of the models themselves, but by the haste of their release.